The most important things at a glance:
-
Learn how athlete's foot and nail fungus differ.
-
Learn how to recognize a fungal infection and how to care for it.
-
Discover tips for targeted prevention and accompanying care.
Athlete's foot and nail fungus – two common, often confused topics
Athlete's foot (tinea pedis) and nail fungus (onychomycosis) are among the most common forms of fungal infections of the skin and nails. Although they share similar risk factors, they differ in their severity and appearance.
Athlete's foot primarily affects the skin, typically between the toes.
Nail fungus changes the structure and appearance of the nails, mostly on the feet.
Both phenomena should be recognized early and accompanied by coordinated care in order to stabilize the nail and skin condition.
Athlete's foot: Recognize symptoms & know causes
Athlete's foot is a common and unpleasant condition caused by certain types of fungi . To effectively combat athlete's foot , it is important to recognize its symptoms early and understand the causes . This not only helps with treatment but also with prevention.
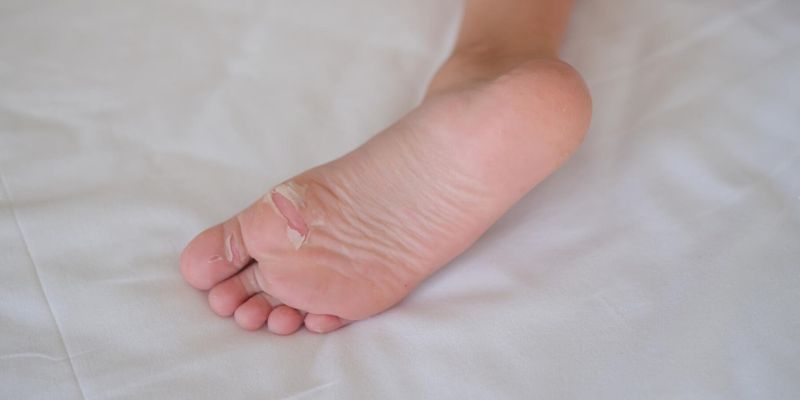

Symptoms of athlete’s foot:
Early detection of athlete's foot symptoms is key to preventing more serious skin problems. Here are the most common signs to look out for:
-
Itching and burning between the toes: Often the first sign of athlete's foot.
-
Redness and swelling: Affected areas may be red, swollen, and warm.
-
Scaly skin: The skin between the toes or on the soles of the feet may be flaky and cracked.
-
Blisters: Sometimes small blisters form that can be itchy or painful.
- Odor development: Infected feet can develop a strong, unpleasant odor.
Athlete’s foot causes:
To effectively treat athlete's foot and prevent it from occurring in the future, it is important to know the causes of this infection:
-
Humid environment: Fungi thrive in warm, humid environments such as swimming pools, showers, and locker rooms.
-
Direct contact: Walking barefoot in communal spaces can increase the risk of infection.
-
Poor foot hygiene: Inadequate drying of the feet after washing promotes the development of fungi.
-
Weakened immune system: People with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to infections such as athlete's foot.
- Tight shoes: Wearing shoes that are too tight or poorly ventilated can worsen the foot climate and promote the formation of fungi.

Schutz, Pflege & Hygiene bei Fuß- und Nagelpilz
Ideal für die tägliche Pflege der Füße
Bestehend aus natürlichen Wirkstoffen
The 3 stages of athlete's foot: Which symptoms occur when?
Athlete's foot develops through different stages , each with its own symptoms. Recognizing these stages can be crucial for initiating proper treatment early and thus preventing more serious complications.
Early stage:
-
Severe itching: This is often the first sign and occurs particularly frequently between the toes.
-
Flaky skin: The skin in this area becomes flaky, which can lead to further dryness and cracking.
- Red spots on the skin: These begin to flake and can spread across the feet.
Advanced stage
-
Cracks in the skin: These initially form in the cornea and can be painful, especially when walking.
-
Weeping skin: Untreated areas begin to ooze, which can cause pain and discomfort.
- Pain when walking: The pain can be intense and is often a sign that the condition is advanced.
Late stage:
-
Broken blisters: When blisters burst, they create open wounds, which facilitate the spread of fungal spores and other pathogens.
-
Erysipelas: A serious bacterial infection that often occurs between the toes, where athlete's foot is also common.
- Chronic skin changes: Long-term athlete's foot can cause permanent skin damage. The skin may become thicker and permanently scaly, cracked, or discolored.
To prevent this from happening, it is important to act immediately at the first signs of athlete's foot to prevent the spread and progression of the infection.
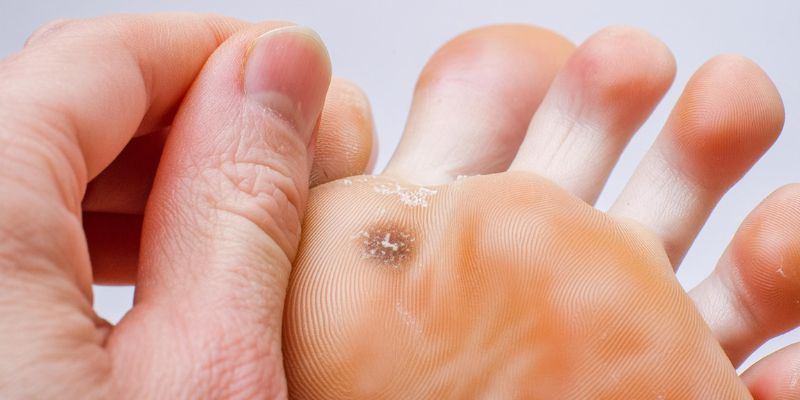
What types of athlete's foot are there?
Athlete's foot is caused by several different types of fungi that differ in their behavior and preference for specific areas of the body. Doctors identify three main types of fungi that can cause athlete's foot in humans:
Filamentous fungi (dermatophytes), yeast fungi and very rarely mold fungi.
-
Dermatophytes are the most common pathogens that cause athlete's foot. They possess a special enzyme that can break down keratin—a substance found in abundance in the calluses, hair, and under the fingernails and toenails. Dermatophytes feed on this horny substance and therefore prefer places where they find it in large quantities.
-
Mold fungi are extremely rare in athlete's foot infections and usually only occur in combination with other fungal species. They cannot break down the human keratin substance on their own, but are occasionally found on already infected skin areas, for example, through contact with contaminated soil.
- Yeast fungi, especially the most common example, Candida albicans , prefer a warm, moist environment and are therefore more commonly found between the toes or in other skin folds. In addition to the skin, they can also infect mucous membranes and the digestive tract.
The different pathogens lead to different types of athlete's foot , which differ in specific symptoms and manifestations .
In the next section, we will discuss in detail the characteristic features of each type of athlete's foot.
Interdigital mycosis: The athlete's foot in the spaces between the toes
Interdigital mycema, also known as tinea pedis interdigitalis , is a common form of athlete's foot that primarily manifests itself between the toes .
This condition can cause discomfort and discomfort, so it is important to recognize symptoms early.
-
Itching and burning: The affected areas between the toes may itch intensely and cause a burning sensation, which is often the first sign of this mycosis.
-
Redness: Redness develops between the toes, which may indicate inflammation.
-
Flaky skin: The skin between the toes becomes flaky and may begin to peel off, causing further irritation.
-
White blisters between the toes: Small white blisters may appear, indicating a worsening of the infection and may become inflamed.
- Bad smell: An unpleasant smell is often an accompanying symptom, as the moist environment promotes the proliferation of fungi.
Moccasin mycosis: Widespread athlete's foot infection
Moccasin mycosis, also known as tinea pedis plantaris , is another form of athlete's foot that affects the soles and sides of the feet .
This type of athlete's foot can be persistent and often requires longer treatment than other forms. The fungus can also spread to the edges and tops of the feet.
-
Extensive redness and scaling: The skin on the soles of the feet and heels becomes red and scaly, often changing the overall appearance of the sole of the foot.
-
Thick, dry skin: The skin appears thicker and drier than usual, similar to a callus, which can cause discomfort when walking.
-
Cracks in the skin: Dryness can cause cracks, which can be painful and increase the risk of secondary infections.
- Itching: Despite the dry appearance, severe itching may be present, which affects daily well-being.
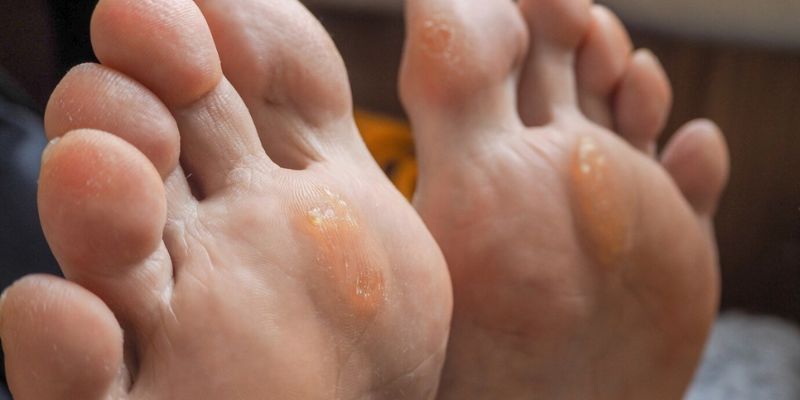
Vesicular-dyshidrotic: The dangerous little blisters
Vesicular dyshidrotic mycosis is a form of athlete's foot characterized by small, fluid-filled blisters that can occur primarily on the soles of the feet or on the sides of the fingers.
This type of infection can be particularly painful and requires immediate treatment.
-
Small blisters: Small, clear blisters filled with fluid form on the skin and often appear in groups.
-
Itching and burning: The affected areas may itch severely and cause burning, especially when the blisters burst.
-
Redness and inflammation: Redness and inflammation may occur around the blisters, increasing the risk of bacterial infection.
-
Pain when walking: Due to the placement of the blisters on the soles of the feet, sufferers may experience pain when walking or standing.
- Peeling skin: After the blisters burst, the skin may begin to peel off, causing further discomfort.
What is nail fungus?
Nail fungus, medically known as onychomycosis , is a common fungal infection that affects the nails of the hands and feet . The infection often begins at the edge of the nail and slowly spreads to the nail bed.
Typical symptoms are
- discoloration,
- Thickenings
- and brittleness of the nails l .
These nail changes can make the nail look unsightly and even painful. Nail fungus is caused by various fungal species, including dermatophytes, yeasts, and molds, and can be transmitted through direct contact or contaminated surfaces .
To learn more about effective treatment options, read our guide on treating nail fungus .

Schutz, Pflege & Hygiene bei Fuß- und Nagelpilz
Ideal für die tägliche Pflege der Füße
Bestehend aus natürlichen Wirkstoffen
Athlete's foot and nail fungus: Differences & similarities
Athlete's foot and nail fungus are both common fungal infections that are caused by similar conditions, but differ in their specific characteristics and treatment approaches.
➽ Scientific name:
- Athlete's foot: Tinea pedis
- Nail fungus: Onychomycosis
➽ Trigger:
- Athlete's foot: Is usually caused by the filamentous fungus Trichophyton, less frequently by other filamentous, yeast, budding or mold fungi.
- Nail fungus: Often caused by filamentous fungi (dermatophytes), occasionally also by yeast or mold fungi.
➽ Causes:
Both conditions are favored by similar factors, such as:
- Generally weaker immune system.
- Older people are more often affected.
- Walking barefoot in public, warm and humid places such as saunas or swimming pools.
Specific causes of athlete's foot also include skin injuries caused by ill-fitting shoes or incorrect foot care .
Specific causes of nail fungus are often shoes that are too tight or have damp inside, which, for example, remains damp due to heavy sweating.
➽ Symptoms:
Athlete’s foot:
- Often begins between the toes with itching, redness and scaling.
- May develop blisters and small pustules.
- In the advanced stage, cracks and skin injuries occur.
Nail fungus:
- The nails become brittle and show streaks, spots or discoloration.
- This leads to a thickening of the nail plate and possibly inflammation of the nail bed .
Both types of fungi require specific treatments tailored to the type of fungus and the stage of the infection. Athlete's foot can often be treated topically, while nail fungus may require more intensive and often systemic treatment.
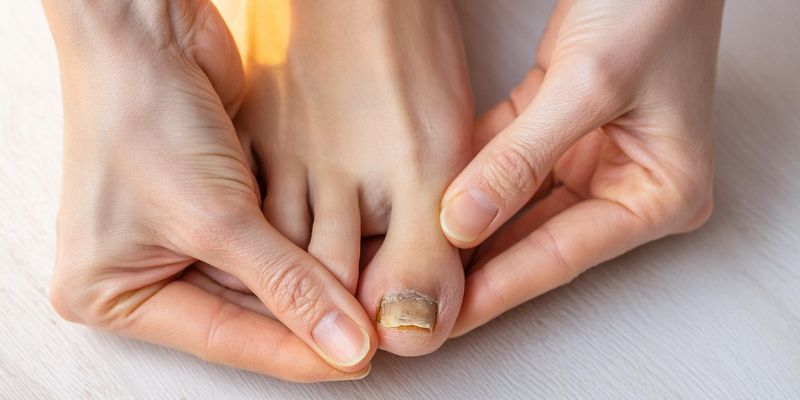
How contagious are nail fungus and athlete's foot really?
Nail fungus and athlete's foot are highly contagious and can easily be transmitted from one person to another , especially in warm, humid environments such as swimming pools, saunas, and locker rooms.
Transmission occurs through direct skin contact or through contact with contaminated surfaces such as towels, shoes or floors.
Why risk groups should be particularly careful
People with a weakened immune system, diabetes or circulatory problems have an increased risk of developing athlete's foot or nail fungus.
Elderly people and those who frequently spend time in humid and warm environments such as swimming pools or saunas should also be particularly careful.
It is important that those at risk take preventive measures to avoid fungal infections and seek immediate medical attention if signs of athlete's foot or nail fungus appear.
Foot and nail fungus: The risk of a chronic disease
Athlete's foot and nail fungus can become chronic conditions if not treated properly. Chronic fungal infections can recur and be more difficult to treat.
They can also lead to complications, such as secondary bacterial infections. Therefore, it is important to detect fungal infections early and treat them consistently to reduce the risk of chronic disease.
Treating athlete's foot: These are the options
Athlete's foot can be treated in a variety of ways, depending on the severity of the infection and individual needs.
Topical treatments such as creams, ointments, or tinctures are the most common first steps to combat symptoms. These products contain active ingredients specifically designed to eliminate fungal spores and prevent the spread of the infection.
For more persistent cases, or when the nails are also affected, oral medications that work internally against the fungus may be prescribed. It is important that any treatment be applied consistently and continued even after symptoms have subsided to prevent relapses.
Pamper your feet: Discover our foot bath salts from Health Routine
Our feet carry us through life and therefore deserve the best care, especially when they're affected by athlete's foot and nail fungus. The foot bath salts from Health Routine not only offers cosmetic support for the care of foot and nail fungus, but also ensures a refreshing and soothing skin feeling.

Schutz, Pflege & Hygiene bei Fuß- und Nagelpilz
Ideal für die tägliche Pflege der Füße
Bestehend aus natürlichen Wirkstoffen
The ingredients of the salt , such as
- Sea salt,
- Baking soda
- and essential oils such as tea tree, eucalyptus and peppermint oil,
use their cleansing and antimicrobial properties to soothe the skin and balance the skin environment.
The application is simple:
- Dissolve 2-3 tablespoons of salt in warm water
- and let your feet soak in it for at least 10 minutes.
This relaxing ritual helps promote well-being and sustainably supports the health of the feet.
Treating athlete's foot and how you can support healing
Effective treatment of athlete's foot combines drug therapies with supportive care measures to accelerate the healing process.
Thorough foot hygiene is essential; daily foot baths with antifungal additives and regular foot examinations help monitor and adjust the healing process.
Avoid skin irritations caused by harsh skincare products and choose gentle, skin-friendly alternatives instead.
Stress reduction through yoga or meditation also strengthens the immune system and promotes healing. A nutrient-rich diet rich in vitamins and minerals such as zinc and vitamin C also supports healthy skin and nails.
Please also check out this article: 10 vitamins for healthy nails » What you should know!
Athlete's foot: Why treatment takes more time
Treating athlete's foot can take more time than treating nail fungus. This is because the fungi can penetrate deep into the skin and are harder to reach.
Treatment can take several weeks to months , depending on the severity of the infection and the type of fungus causing it. It's important to continue treatment consistently until the infection is completely cleared.
Are you interested in more tips for healthy and beautiful nails? Read our guide on the topic Healthy Nails to learn more about proper care and nutrition for strong nails.
What treatments are effective for both types of fungal infections?
There are various ways to treat athlete's foot and nail fungus, including creams, ointments, and tablets. Nail Care Pen from Health Routine can be used as a supportive cosmetic treatment for nail fungus. It contains natural ingredients in a carefully balanced formula and combines
- tea tree oil,
- Aloe Vera,
- lemon juice
- as well as vitamin E and vitamin C.

Pflegt auch kosmetisch bei Nagelpilzinfektion
Spendet Feuchtigkeit & regeneriert
Schützt & stärkt die Nägel
This active ingredient complex can help nourish and moisturize nails. If you want to treat both athlete's foot and nail fungus simultaneously, the Health Routine cosmetic nail care products can be a helpful addition:
✔ Health Routine Nail Care Pen : Care for and protect your nails daily with the Health Routine Nail Care Pen, your cosmetic companion for fungal nail infections.
✔ Health Routine Foot Bath Salts : Provides protection, care, and freshness for your feet. The power of essential oils and sea salt supports the fight against bacteria and fungi. It also prevents calluses and cracked feet .
✔ Health Routine Feet Care Spray : Contains natural ingredients such as aloe vera, tea tree oil and lavender oil to provide your feet with optimal care and hygiene and effectively combat sweat odor.
Preventing nail fungus and athlete's foot: These are the most helpful tips
-
Keep your feet dry: Keep your feet as dry as possible. Dry them thoroughly, especially between the toes, after showering or if they get wet.
-
Use antimicrobial foot powder: Foot powder can help keep feet dry and reduce the risk of fungal infections. Sprinkle the powder into socks and shoes, especially before exercise.
-
Wear breathable shoes and socks: Choose shoes and socks made of breathable materials such as cotton or special moisture-wicking fabrics. These materials effectively wick away moisture and help prevent fungal growth.
-
Change your shoes and socks regularly: Avoid wearing the same shoes two days in a row. Give your shoes time to air out, which reduces the risk of fungal growth.
-
Protect your feet in public areas: Always wear shoes in public changing rooms, showers, and swimming pools to avoid direct contact with fungal spores.
- Regular foot hygiene: Clean your feet regularly and make sure you keep them clean at all times. Good foot hygiene is crucial for preventing fungal infections.
These simple but effective tips can help prevent both nail fungus and athlete's foot, thus ensuring the long-term health of your feet.
Conclusion
The treatment and prevention of athlete's foot and nail fungus is crucial for maintaining foot health. A combination of
- proper hygiene,
- suitable care products
- and attentive self-observation forms the basis for effective results.
It is important to act quickly at the first signs of infection to prevent its spread and avoid long-term complications.
In addition to medical treatment and good foot hygiene, special foot baths, such as our foot bath salts from Health Routine , can also be used to promote the well-being of the feet.
FAQ
What can you do against athlete's foot with home remedies?
Home remedies can be used as a supportive measure in the treatment of athlete's foot. One popular home remedy is a foot bath with apple cider vinegar, which may have antifungal properties due to its natural acidity.
Rubbing tea tree oil on the affected areas is also often recommended, as it is known for its antimicrobial properties. However, home remedies alone are usually not enough to completely cure athlete's foot, so a visit to the doctor and additional treatment with medically approved antifungals is advisable.
How long does it take to treat athlete's foot?
The duration of treatment for athlete's foot can vary depending on the severity of the infection and the treatment method used. Typically, treatment with topical antifungals, such as creams or sprays, lasts about 4 to 6 weeks.
In more severe cases, where oral medication may be required, treatment may take longer. It is crucial to follow the instructions of your doctor or pharmacist and not to stop treatment prematurely, even if symptoms subside.
How long does the treatment for nail fungus take?
Treatment for nail fungus is generally more lengthy than for athlete's foot. Topical treatments can take several months, while oral therapy typically takes between 6 and 12 weeks.
Because nail fungus can penetrate deep into the nail, patience is required, and complete healing often only occurs with the regrowth of a healthy nail. Regular monitoring by a specialist is recommended to assess the progress of treatment.
Your medical advice
Our products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. The information provided in this article is for informational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for advice from your physician or other healthcare professional.
Furthermore, our products are not a substitute for medication or other treatment prescribed by your doctor or healthcare provider. Regardless of the due care taken, no liability or warranty is assumed for the
- Accuracy,
- topicality,
- completeness
- and availability of the information provided.
No legal claims can be made for any damages potentially resulting from the use and application of this information. Liability claims of any kind are excluded.